Overview
- Introduction: Understanding Flood and Landslide Risks in Nepal
- The Science Behind Floods and Landslides
- Stories from the Ground: First-Hand Accounts
- The Impact on Communities and Livelihoods
- What Is Being Done: Disaster Preparedness and Responses
- Climate Change and Future Risks
- How Can You Help: Community Involvement and Support
- Conclusion: Building a More Resilient Nepal
- Gallery
Overview
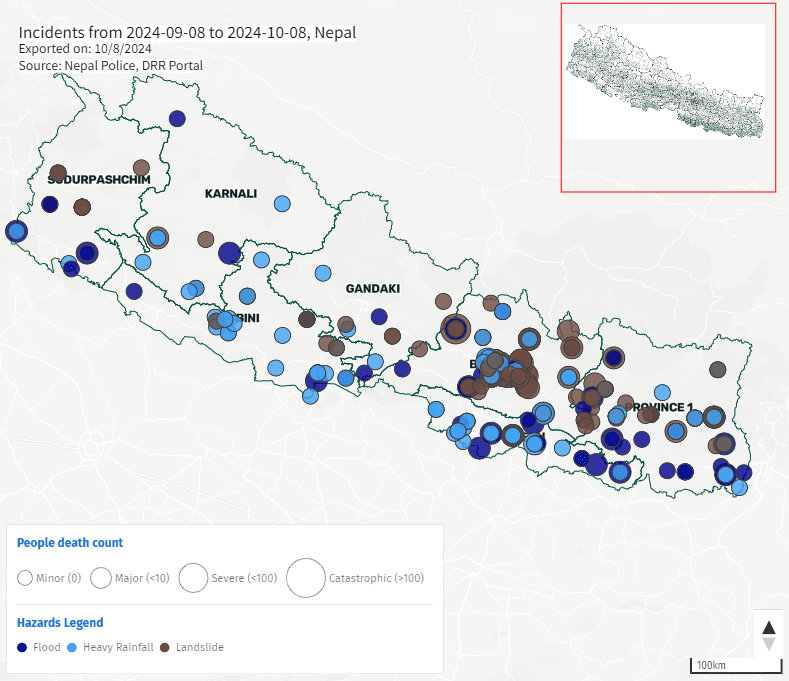
Nepal’s unique geography, characterised by its towering mountains and fertile plains, faces significant challenges during the monsoon season. Every year, severe floods and landslides wreak havoc on vulnerable communities, especially in the Terai and hilly regions. The monsoon of 2024 has been particularly devastating, resulting in 246 lives lost, 15 individuals missing, and over 17,000 people rescued. Tragically, about 3,000 homes have been damaged or destroyed, along with over 100 kilometres of roads and more than 50 bridges rendered unusable. The urgency for community support and resilience is more significant than ever.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Lives Lost | 246 |
| Individuals Missing | 15 |
| People Rescued | Over 17,000 |
| Homes Damaged/Destroyed | About 3,000 |
| Roads Affected | Over 100 kilometres |
| Bridges Unusable | More than 50 |
source: Bipad portal Nepal
The Science Behind Floods and Landslides
Floods in Nepal are primarily caused by heavy monsoon rainfall, while steep slopes, deforestation, and poor land management often lead to landslides. Climate change intensifies these disasters by causing unpredictable rainfall patterns and glacial melting. The 2024 floods highlighted how deforestation increases runoff and soil erosion, particularly in critical watersheds.
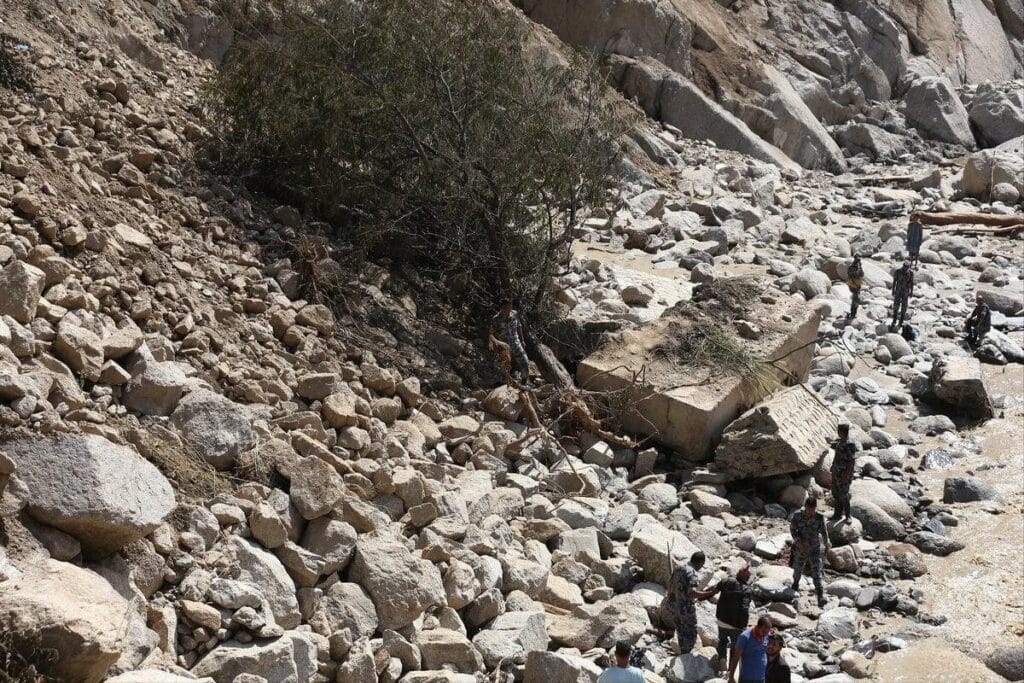

Case Studies
Here are some poignant stories from those affected by the recent disasters:
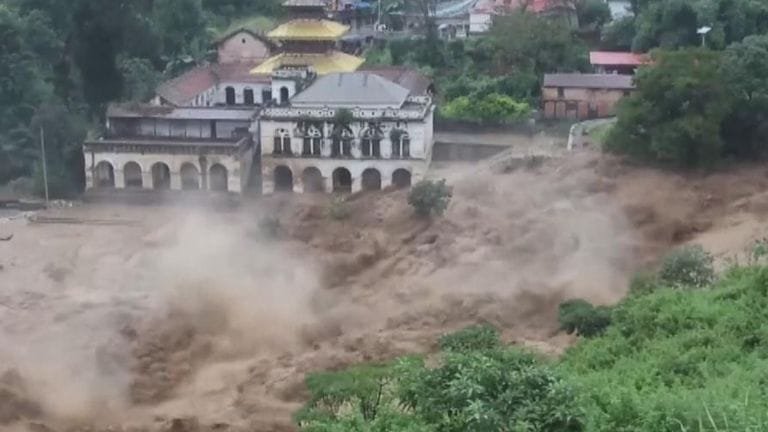
- Sita Tamang, a resident of Sindhupalchok, shared her heartbreaking experience: “When the landslide struck, it felt like the mountain came alive. We lost our home and two family members in an instant. Now, we live in a temporary shelter with nothing but the clothes on our backs.”
- Ramesh Yadav from the Terai region recounted, “We managed to escape with our lives, but our fields were completely submerged. We are left with nothing. The government assistance has been slow, and we need urgent help.”

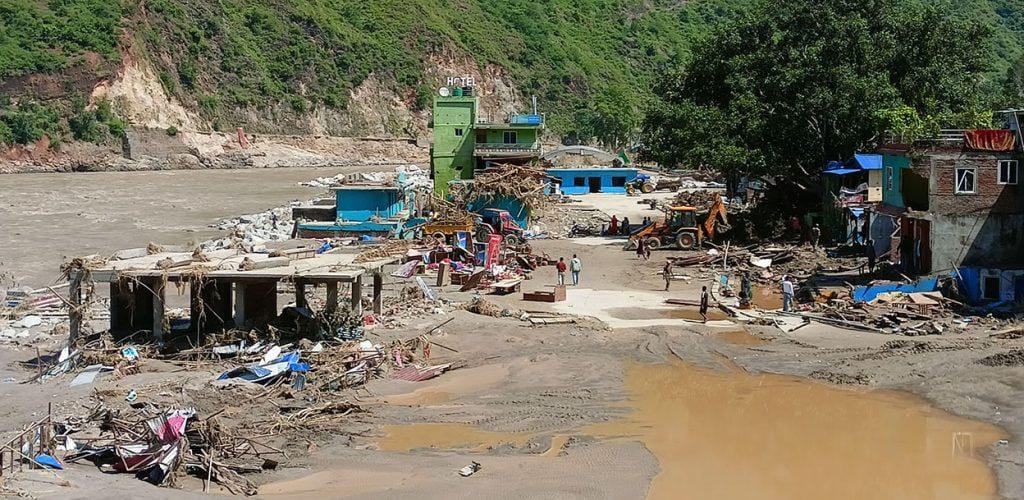
Economic Losses
The economic fallout from the recent floods and landslides is staggering. Vital agricultural areas have been devastated, resulting in losses estimated at NPR 25 billion. The destruction of infrastructure, including over 3,000 homes, 100 kilometres of roads, and more than 50 bridges, has severely disrupted daily life for thousands.

Government Initiatives
The Nepalese government has initiated disaster management efforts, such as the Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act. However, challenges remain, particularly in remote areas. While early warning systems have been set up, many communities must know these alerts.
NGO Efforts
Organisations like the Nepal Red Cross Society and Oxfam have mobilised to provide emergency relief, including food, clean water, and temporary shelters. They emphasise the importance of community training to enhance preparedness for future disasters.

Long-term Outlook
The effects of climate change are undeniable, with projections indicating that Nepal could face an increase in the frequency of natural disasters. Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns can lead to more severe flooding and landslides in the future.
Expert Opinion
Dr Binod Adhikari, a climate scientist, warns: “If current trends continue, we will see not just an increase in natural disasters but a significant threat to human lives and livelihoods in Nepal.”
Volunteer and Donation Information
You can support local communities affected by these disasters by donating to reputable NGOs like the Nepal Red Cross Society or volunteering for reconstruction efforts.
Hopeful Outlook
Despite the devastation wrought by floods and landslides, the resilience of the Nepalese people shines brightly. The country can rebuild and prepare for future challenges with adequate support and proactive measures.


 Member of
Member of